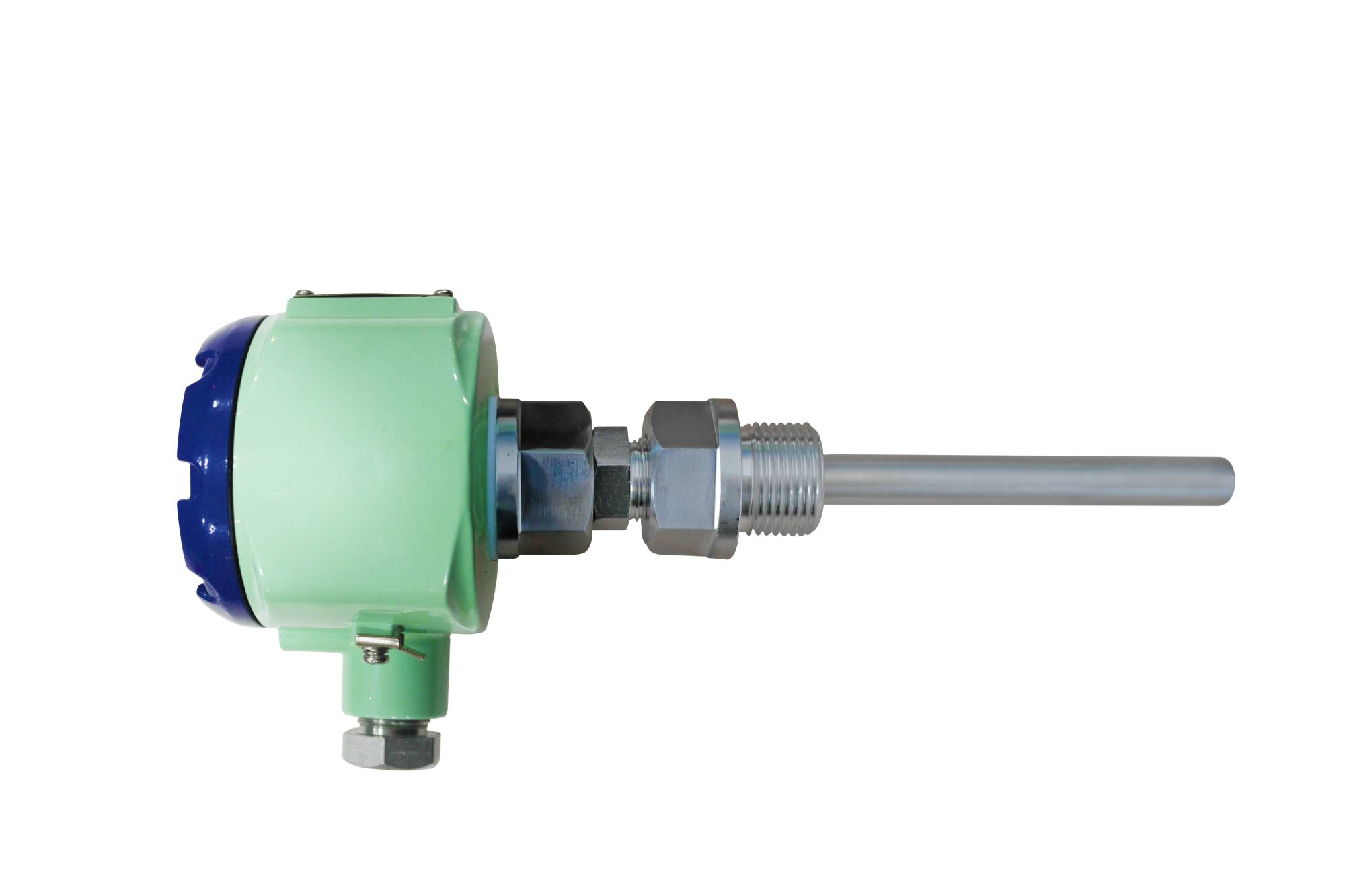
Temperature transmitter
2 month agoThe basic working principle of the temperature transmitter revolves around the temperature sensor. Common temperature sensors such as thermistors use the property that their resistance value changes with temperature. When the ambient temperature changes, the lattice structure of the thermistor changes, causing the electron motion state to change, and then the resistance value changes. Taking the negative temperature coefficient thermistor as an example, the temperature rises and the resistance value decreases. When the constant current source is used for power supply, the voltage at both ends also decreases. The voltage change is the electrical signal manifestation of the temperature change.
Thermocouples are based on the thermoelectric effect. Two different metal conductors form a closed loop. When the temperatures of the two contacts are different, a thermoelectric potential is generated in the loop. The greater the temperature difference, the greater the thermoelectric potential, and this thermoelectric potential is output as a temperature signal.
The signal conditioning circuit amplifies, filters, and linearizes the weak and easily interfered signal output by the sensor. The amplification circuit increases the signal amplitude, the filtering circuit removes noise interference, and the linearization circuit corrects the nonlinearity of the sensor output, so that its output is a standard signal with an accurate linear relationship with the temperature, such as a 4-20mA current signal or a 0-5V voltage signal, which is convenient for subsequent transmission and processing.
Its core advantage lies in high-precision measurement. The carefully calibrated and optimized sensors and signal processing circuits can achieve temperature measurements with an accuracy of ±0.1℃ or even higher, providing reliable data for scientific research experiments, electronic manufacturing and other fields that require strict temperature accuracy. Moreover, the temperature transmitter has a simple structure and relatively low cost. While ensuring performance, it has a good cost-effectiveness and is widely used in various industrial and civilian scenarios.
| Input: | Thermocouple K, E, B, S, T, J, N thermal resistor Pt100Cu100Cu50 (three-wire or four-wire) |
| Output: | Output 4~20mA DC signal within the range. Linear with the millivolt signal of the thermocouple input: Linear with the input resistance signal of the thermal resistor. Linear with the temperature signal. Isolation temperature transmitter·Isolation between input and output, isolation voltage is 0.5KV Increase the ability to resist common mode interference, more suitable for computer networking. |
| Basic error: | *±0.5%F·S |
| Transmission mode: | two-wire system |
| Working power supply: | The transmitter working power supply voltage is minimum 12V, maximum 35V, and the rated working voltage is 24V. |
| Load: |
The limit load resistance is calculated as follows:
RL(max)=50(Vmin-12 (i.e., at 24V, the load resistance can be selected in the range of 0~600Ω) Rated load 250Ω
Normal working environment: a) Ambient temperature: -25℃℃~80℃℃ (conventional type)-20°℃~70°℃ (digital display type)
b) Relative humidity: 5%~95% c) Mechanical vibration: f≤50Hz, amplitude <0.15mm d) The surrounding air does not contain media that corrode chromium, nickel plating, non-ferrous metals and other alloys. |
| Ambient temperature effect: | ≤0.05/1℃ |
| Note: | "*" If the user has special needs, a protocol product with an allowable error of ±0.2% can be provided. |


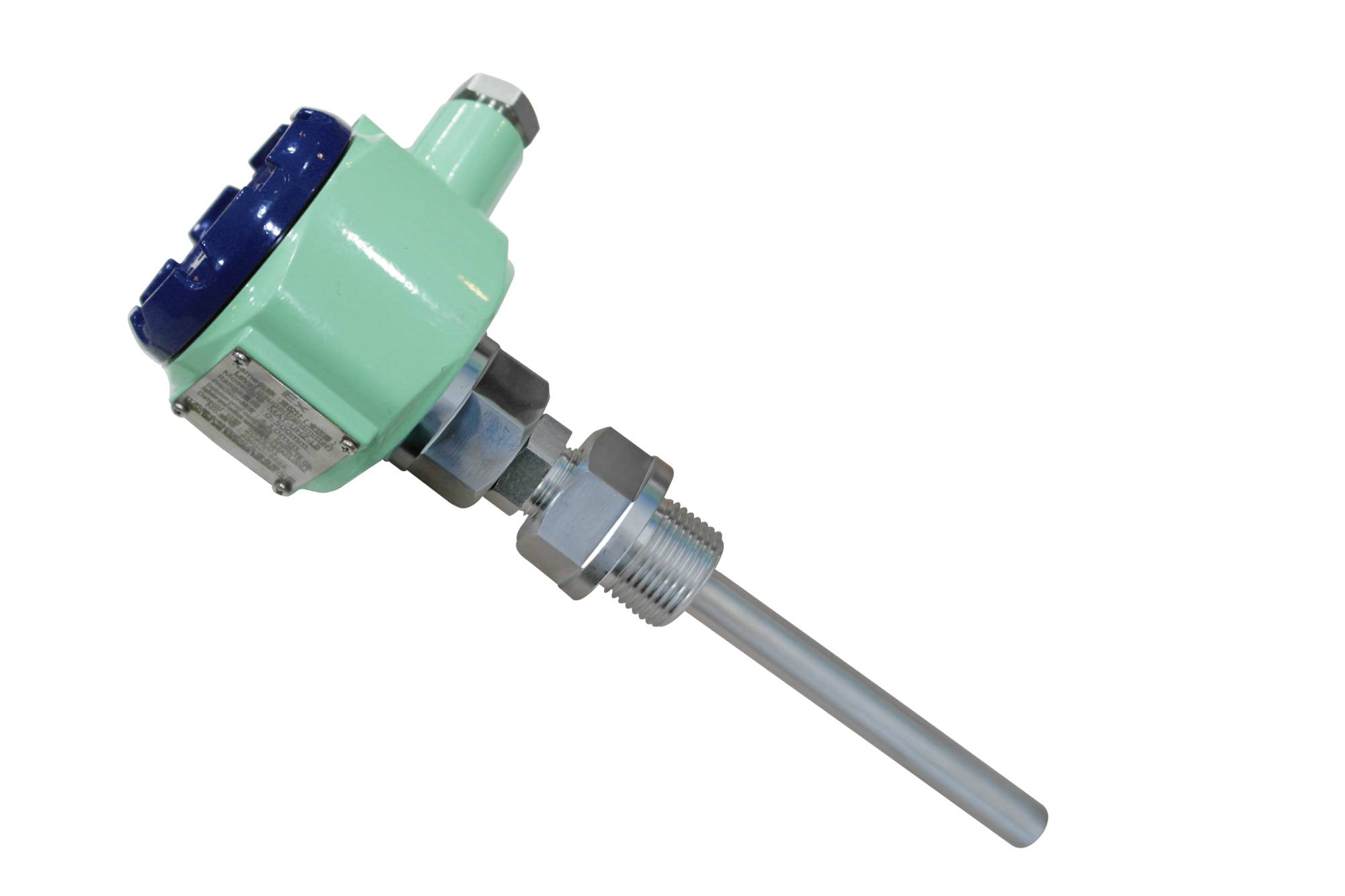
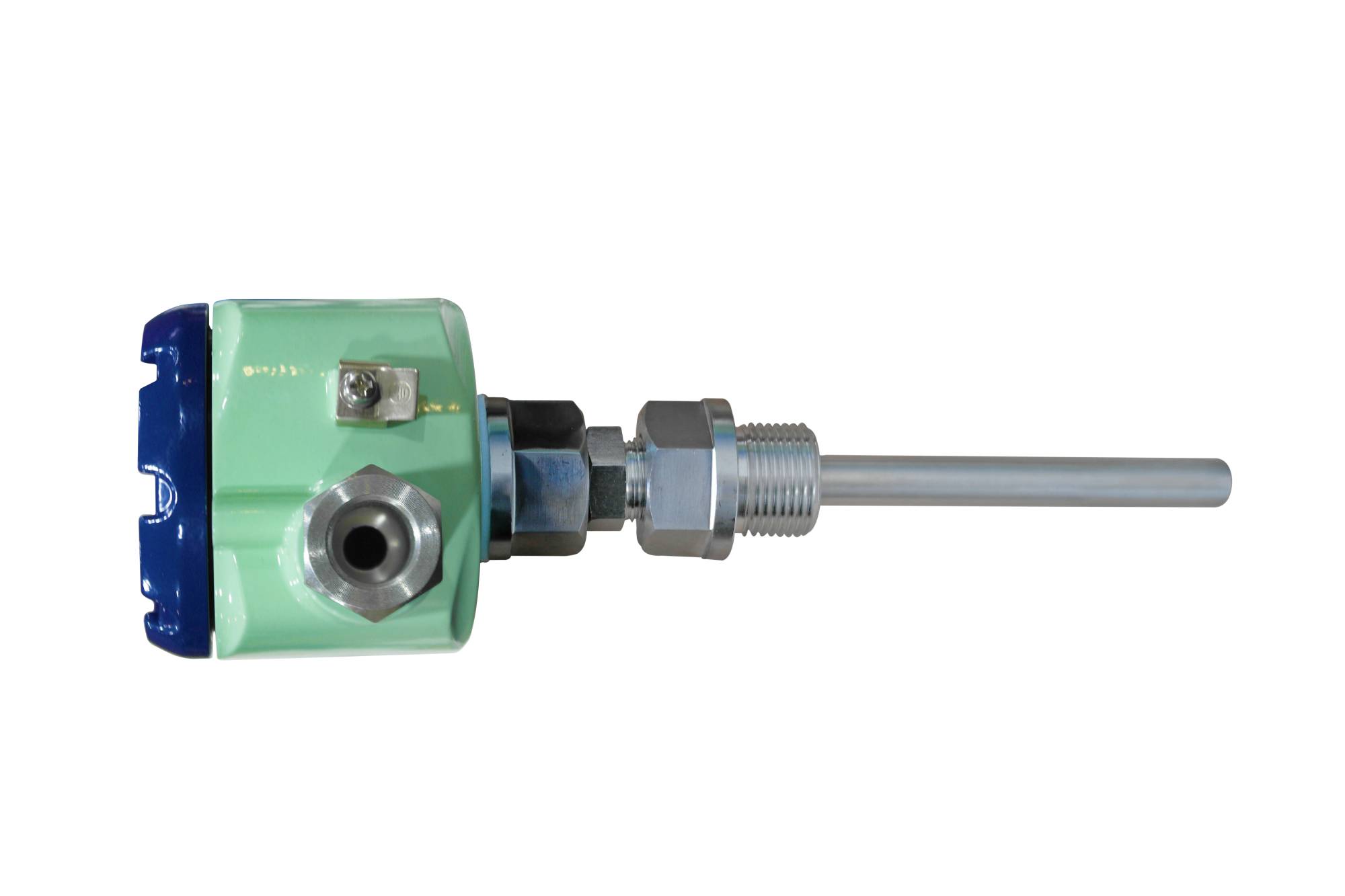
Similar Video Recommendation
You May Also Like
If you are interested in the product, contact Bossgoovideo.com for more information
- *To:
- Jiangsu Meiante Technology Co., Ltd
- *Message:
-
Submit
Main Product:
Pressure transmitter,
Liquid level meter ,
Temperature transmitter,
Flowmeter,
valve,
Wire and cable



















